Table of Contents
- Hearing Loss Infographic Hearing Loss Facts - vrogue.co
- 3 Questions to Ask About Hearing Loss - UCI Audiology
- An audiological profile of a cohort of school-aged children with HIV ...
- Frontiers | Time course of auditory streaming: do CI users differ from ...
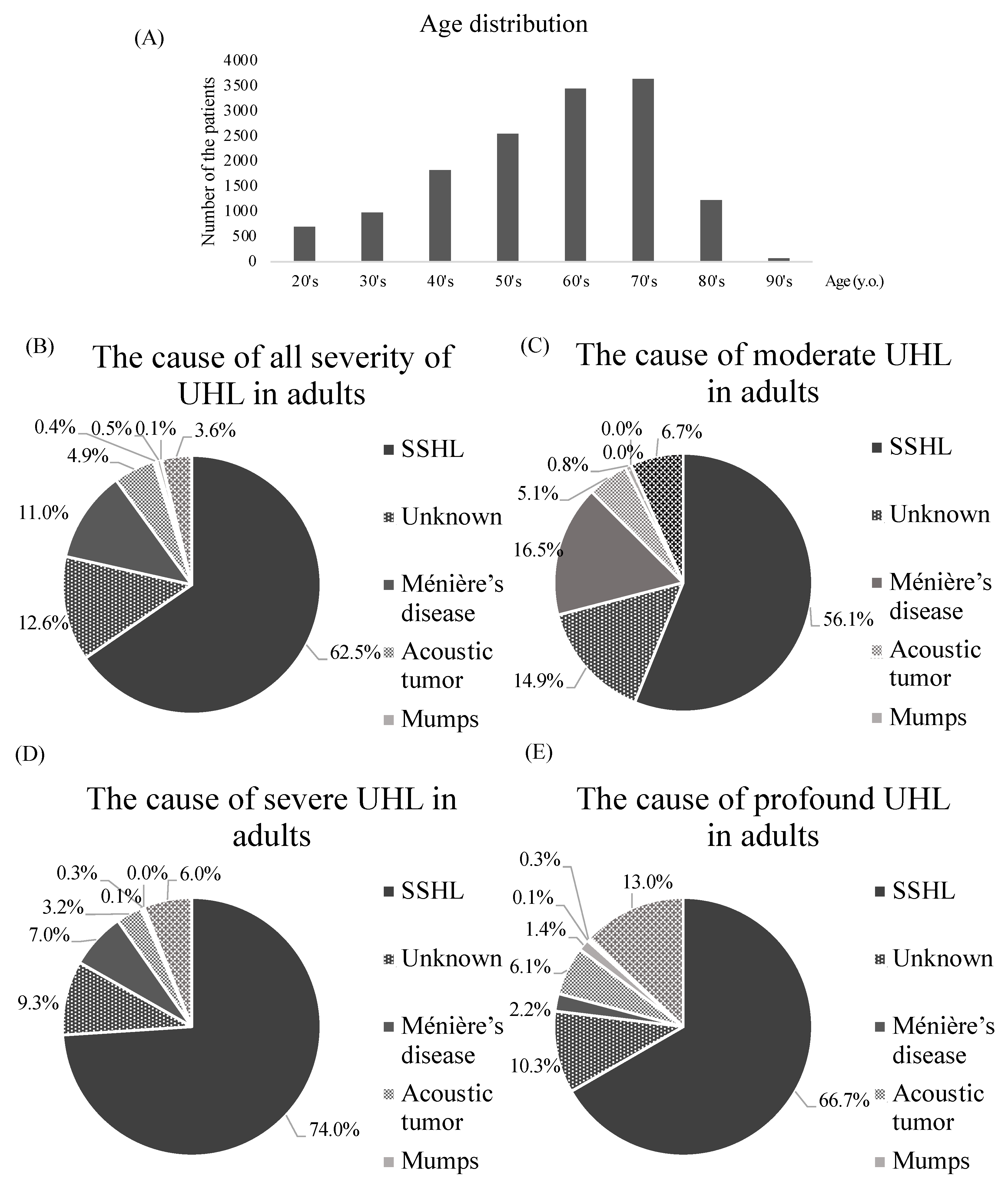
- JCM | Free Full-Text | Etiology, Severity, Audiogram Type, and Device ...
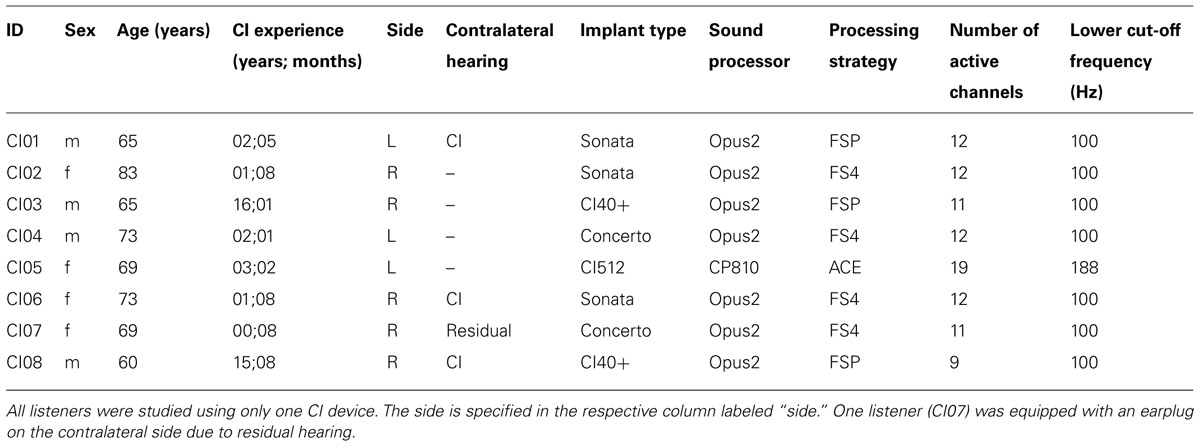
- Demographics concerning the UCI group, in particular etiology of ...
- Lesser Known Facts About Hearing Loss [Infographic] - Resonance Audiology
- How Common is Hearing Loss? – Audiology Infographic - UCI Audiology
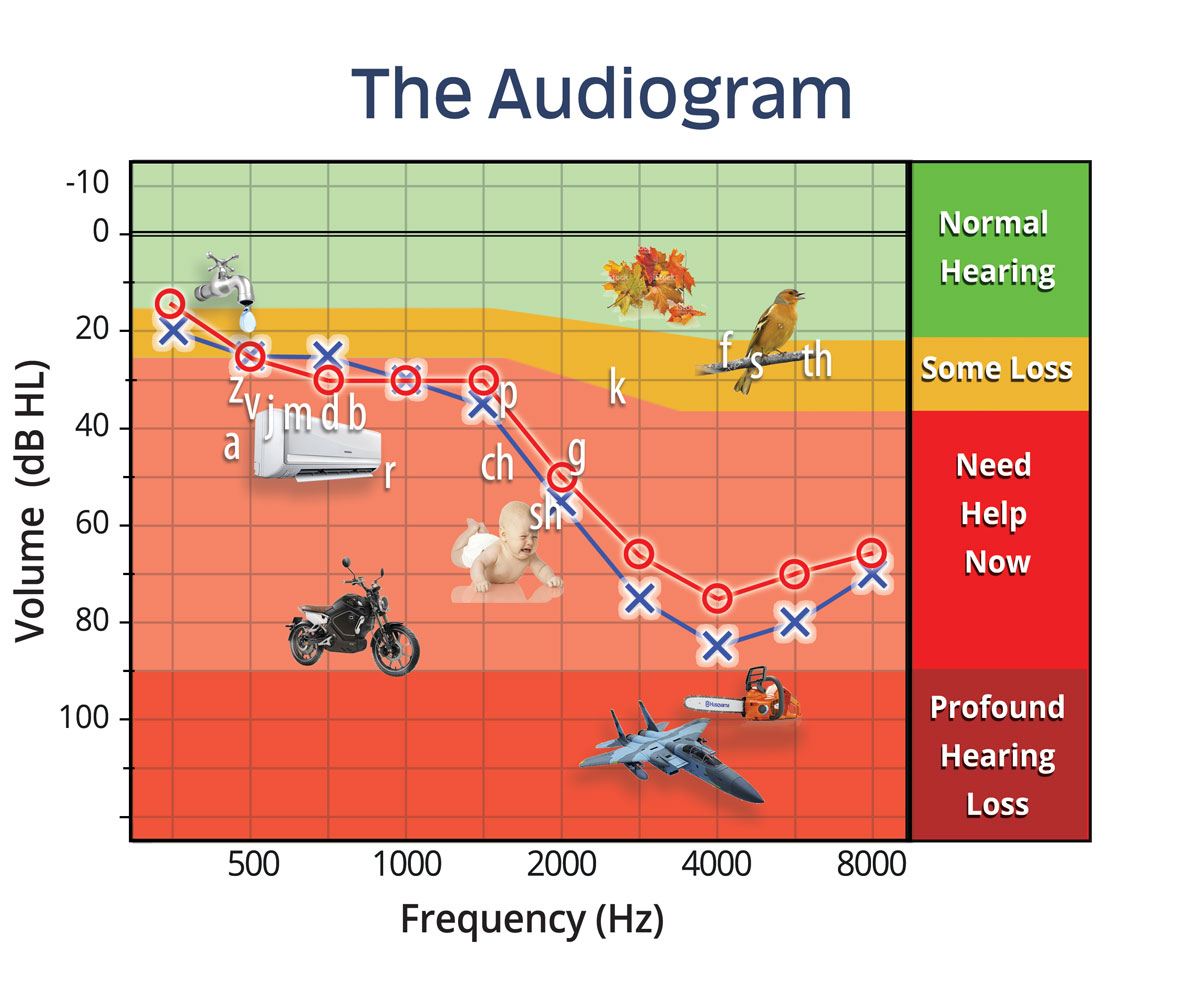
- Understanding An Audiogram Specsavers New Zealand - vrogue.co
- Infographics Images

What are Comorbidities?

![Lesser Known Facts About Hearing Loss [Infographic] - Resonance Audiology](https://resonanceaudiology.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/03/ResonanceAudiology.com_Infographic_March2022-233x1024.jpg)

Common Comorbidities Associated with Hearing Loss in Adults



Why is it Important to Address Comorbidities in Adults with Hearing Loss?
Addressing comorbidities in adults with hearing loss is crucial for several reasons: Improved treatment outcomes: By understanding and managing comorbidities, healthcare professionals can develop more effective treatment plans that address the individual's overall health needs. Enhanced quality of life: Treating comorbidities can improve an individual's overall quality of life, reducing the risk of complications and improving their ability to engage in daily activities. Reduced healthcare costs: Managing comorbidities can help reduce healthcare costs associated with untreated hearing loss and related conditions. In conclusion, hearing loss in adults is often accompanied by comorbidities that can have a significant impact on overall health and quality of life. By understanding the relationships between hearing loss and other health conditions, healthcare professionals can develop more effective treatment plans that address the individual's unique needs. The American Academy of Audiology emphasizes the importance of addressing comorbidities in adults with hearing loss, and we encourage individuals to seek professional help if they are experiencing hearing loss or related health issues. By working together, we can improve treatment outcomes, enhance quality of life, and reduce healthcare costs associated with hearing loss and comorbidities.To learn more about PDF hearing loss comorbidities in adults, visit the American Academy of Audiology website or consult with a healthcare professional.